Compiled by Walter Sorochan EmeritusProfessor San Diego State University
Posted August 12, 2015, Updated November 02, 2021. Disclaimer; The information presented here is for informative and educational purposes only and is not intended as curative or prescriptive advice.
What is Whole Food Complex? This article clarifies this term.
Whole food complex is made up of three concepts. The first term is whole foods, the second is complex and the third is packaging of the first two terms as whole food complex. We can now explore what and how each of the three terms fit together.
Whole foods: are foods that are unprocessed and unrefined, or processed and refined as little as possible, before being consumed. Whole foods typically do not contain added salt, carbohydrates, or fat. Bruce: whole food defined 2000 Examples of whole foods include unpolished grains, fruits, vegetables, and animal products, including meats and non-dairy products. Wiki: whole food defined
|
Origin of whole food idea: The earliest use of the term in the post-industrial age appears to be in 1946 in The Farmer, a quarterly magazine published and edited from his farm by F. Newman Turner, a writer and pioneering organic farmer. The magazine sponsored the establishment of the Producer Consumer Whole Food Society Ltd, with Newman Turner as president and Derek Randal as vice-president. Whole Food was defined as ‘Mature produce of field, orchard, or garden without subtraction, addition, or alteration grown from seed without chemical dressing, in fertile soil manured solely with animal and vegetable wastes, and composts there from, and ground, raw rock and without chemical manures, sprays, or insecticides. Its principal aim was to act as a liaison between suppliers and the growing public demand for such food. In 1960 the leading organic food organization called the Soil Association opened a shop in the name selling organic and whole grain products in London, UK. Wiki: whole food defined |
"Diets rich in whole and unrefined foods, like whole grains, dark green and yellow/orange-fleshed vegetables and fruits, seeds, contain high concentrations of antioxidant [ stop formation of free radicals ] phenolics [ rich in acid and odor ], fibers and numerous other that may be protective against chronic diseases. "diet rich in a variety of whole foods has been hypothesized as possibly anti-cancer due to the synergistic effects of antioxidants and phytochemicals common in whole foods. Wiki: whole food defined
Complex:
Complex refers to the many individual substances [ often referred to as co-factors ] that are inter-related and help each other to function as a whole in a food or nutrient. Such a relationship is complicated and hence referred to as complex. Reference to substances, rather than co-factors, is more accurate as no one really has identified all the substances functioning as helpers. Substances that have been identified as co-factors within nature's foods include, but are not limited to: vitamins, minerals, terpenes, trace mineral activators, enzymes, co-enzymes, chlorophyll, lipids, essential fatty acids, fiber, carotenoids, antioxidants, flavonoids, pigments, amino acids, whole proteins, and more.
Food researcher Vic Shayne, Ph.D. clearly describes the complexity of whole food nutrition and how this cannot be duplicated in the lab with vitamin isolates: "Since whole food ingredients are natural, they contain a host of nutrients that exist within a complex. A food complex includes not only vitamins and minerals, but also many cofactors [ helper nutrients ] that are found in nature's foods as a result of the evolutionary process."
Shayne points out that cofactors and food complexes therefore cannot be made in a laboratory nor can they be duplicated by scientists. And many nutritional doctors and researchers agree that cofactors are often more valuable than vitamins and minerals, and that food cannot be duplicated due to its complexity, dynamism, and energy.
The human organism is biologically suited to ingest and utilize nature's whole foods for its sustenance and the optimal functioning of cells, and for the processes of healing and prevention. Because synthetic vitamin and mineral pills are merely comprised of isolated chemicals, the body often regards these as foreign invaders. Therefore, some vitamin, mineral, and amino acid synthetic supplements can produce toxic side effects ranging from skin itching and flushing (niacin, for example) to liver impairment (vitamin A palmitate).
The ingredients within foods operate on a system of synergism; they work as "teams" to feed cells. The interwoven, interrelated, and complementary functions of food particles represent some of nature's most wonderful properties of synergistic power and function. Article by Dreher: Whole food supplements is no longer active.
Whole Food Complex
So what is a whole food Complex ? Whole food complex integrates both ideas, the whole foods and the complex, as parts into a bigger and all encompassing functional concept. The small parts work best when all the parts [ rich natural endowment of nutrient substances ] are present. This concept is a relationship between thee human body and the food we eat. More specifically, it is the number of all essential nutrients and enzymes in food on the one hand, and the other hand, how the body absorbs and uses the food. This is referred to as bioavailability.
The various parts of a natural vitamin complex work together in a synergistic manner. Synergy means that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Separating the group of compounds, as in a synthetic vitamin, converts the synthetic vitamin from a physiological, biochemical, active micronutrient into a disabled, debilitated chemical of little or no value to living cells. The synergy is gone.
Supplement makers typically try to stuff as much as possible in a capsule, telling us that the more we take, the better it is for us. This is simply not the case. As you now know, it is not necessarily the amount of a nutrient you ingest that is important, but its form and how much is bioavailable that counts the most. In fact, remembering that ingesting single nutrients can actually create imbalances in the body, logic would dictate the higher the level of a single nutrient that you take in, the quicker this imbalance will occur.
What all of this means: The potency of a supplement has much more to do with synergy than with actual nutrient levels. It is a combined effect of all the parts of the food, rather than the chemical effect of a single part, that is most important.
 A simplistic way to understand the whole food concept is to illustrate with
the following example: "Plant foods have all the innate enzymes that help a plant
to mature and gradually decompose. For example; It is the banana enzymes
that also give us the sweet taste and appetizing odor as it 's enzymes help to
ripen the banana meat. Yes, we need to eat the banana before the enzymes
decompose or spoil it [ the dark banana in the photo on the right ]. The banana enzymes also begin the digestion of the banana in the
stomach and our digestive enzymes finish the job. The enzymes in a raw
plant food all work as an integrated whole in the banana to provide a complete food
that our bodies recognize, can absorb and use without any side effects.
The inclusion of the enzymes and other unknown substances in the raw banana is
what makes banana a whole food! But cooking destroys the enzymes in the banana,
broccoli, carrots and other foods, as does preparation of processed foods.
A simplistic way to understand the whole food concept is to illustrate with
the following example: "Plant foods have all the innate enzymes that help a plant
to mature and gradually decompose. For example; It is the banana enzymes
that also give us the sweet taste and appetizing odor as it 's enzymes help to
ripen the banana meat. Yes, we need to eat the banana before the enzymes
decompose or spoil it [ the dark banana in the photo on the right ]. The banana enzymes also begin the digestion of the banana in the
stomach and our digestive enzymes finish the job. The enzymes in a raw
plant food all work as an integrated whole in the banana to provide a complete food
that our bodies recognize, can absorb and use without any side effects.
The inclusion of the enzymes and other unknown substances in the raw banana is
what makes banana a whole food! But cooking destroys the enzymes in the banana,
broccoli, carrots and other foods, as does preparation of processed foods.
More Examples: Vitamin E is a complex and is now known to embrace the tocopherol group, the xanthine group, the phospholipid group, the lipositol, and the sex hormone precursors. Another is Vitamin D complex contains D1, D2, D3, D4 and a lot of supporting other vitamins, minerals and unknown substances.
Vitamin C as an example of natural vitamin-complex:
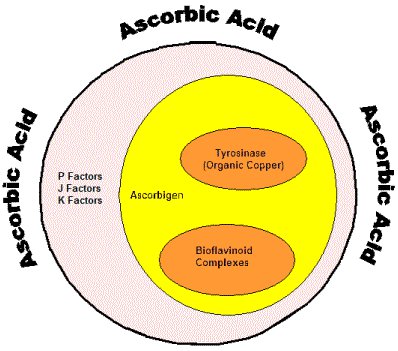
Mother Nature created vitamin C-rich fruits, berries and plants as sodium ascorbate or calcium ascorbate. As you can see in the illustration above, natural Vitamin C has several components, including ascorbic acid, tyrosinase, Vitamin P, Vitamin K and Vitamin J factors, and also ascorbigen and bioflavinoid complexes. Including all the component substances in a plant vitamin C is referred to as a vitamin C-complex or whole food complex. We don't really know all the substances making up a natural vitamin, but the guess is that it could be 50 or more [ We only refer to one of these ]. The illustration above simulates a very small number of essential substances. A vitamin is “a complex assembly of food catalysts, enzymes and unknown substances which must not be altered in structure or proportion of components if it is to retain its function.”
So what are the present day limitations of understanding the whole food complex idea?
Our current understanding of how the whole food complex works is sadly misunderstood. Although nutritionists and some scientists claim to know the amount of vitamins and minerals needed by the body by espousing Recommended Daily Allowances [RDA], these are often best guesses. This is especially true when it comes to their estimates of the best ratio dosage to take minerals; e.g. ratio of calcium to magnesium! Another major RDA flaw is lack of independent research on co-factors and how substances in food help each other.
There is a whole symphony of other substances or micronutrients (phytonutrients or phytochemicals) that work in concert with vitamins and minerals to orchestrate a natural harmony in our bodies. Although more than 25,000 different micronutrients have been discovered in whole fruits and vegetables alone, most of these have not been studied as to their possible implication as co-factors or to bioavailability. As of 1996, over 3,800 different compounds had been identified in foods as having nutritional significance. [. However, in a laboratory, twenty nutrients are about all that modern science can reproduce and put into a vitamin product made in a lab. [ Duke, James Textbook,1992 ] The significance of this information is that we know very little about all the plant substances needed for health. Wiki: other nutrients
The spin on Whole-Food-vitamin complex: The simple spin is that vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, unknown substances and enzymes work together as a team.
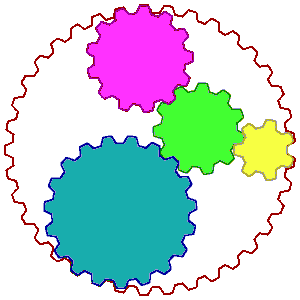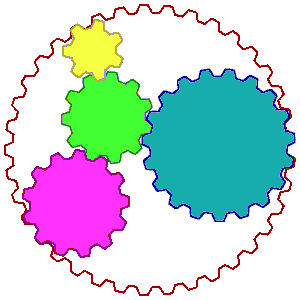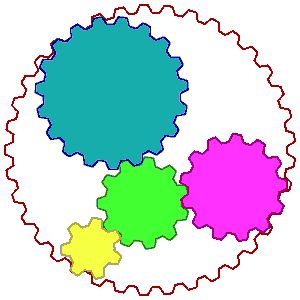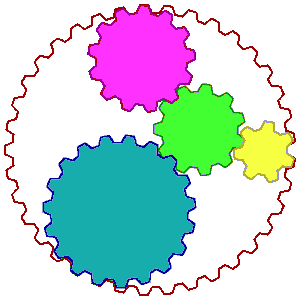 The animation on the left
has been used to illustrate this concept with all the wheels turning.
The nutrient complex is the big outer wheel. The big wheel or complex is
made up of different sized [colored ] gear wheels, each representing a different co-factor
or substance in the proper ratio amount. The main point is
that the different substances [small wheels] are in the appropriate ratios
essential as helpers. The big wheel, or plant nutrient,
works as long as the smaller wheels are present in the proper size or ratio. But
if one smaller wheel is missing or pulled out as an isolate, then the big wheel
complex cannot work! More importantly, neither can the smaller wheels by themselves as in synthetic supplements ]!
The animation on the left
has been used to illustrate this concept with all the wheels turning.
The nutrient complex is the big outer wheel. The big wheel or complex is
made up of different sized [colored ] gear wheels, each representing a different co-factor
or substance in the proper ratio amount. The main point is
that the different substances [small wheels] are in the appropriate ratios
essential as helpers. The big wheel, or plant nutrient,
works as long as the smaller wheels are present in the proper size or ratio. But
if one smaller wheel is missing or pulled out as an isolate, then the big wheel
complex cannot work! More importantly, neither can the smaller wheels by themselves as in synthetic supplements ]!
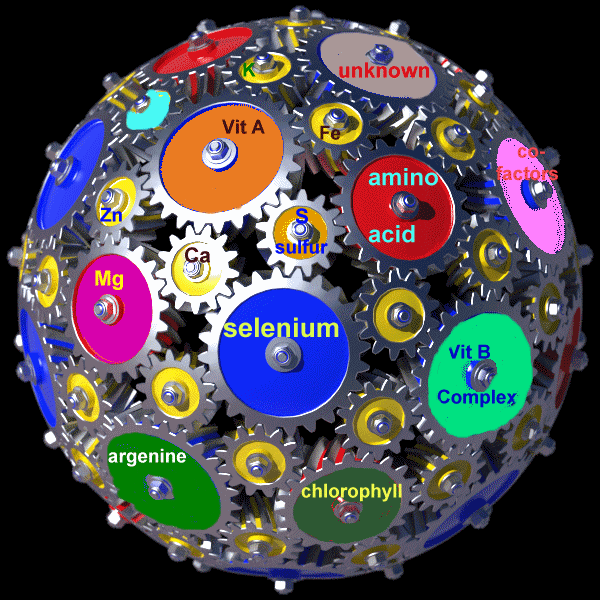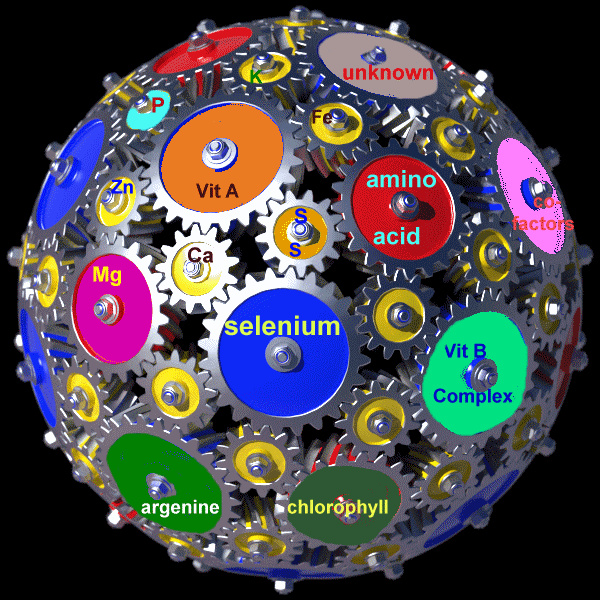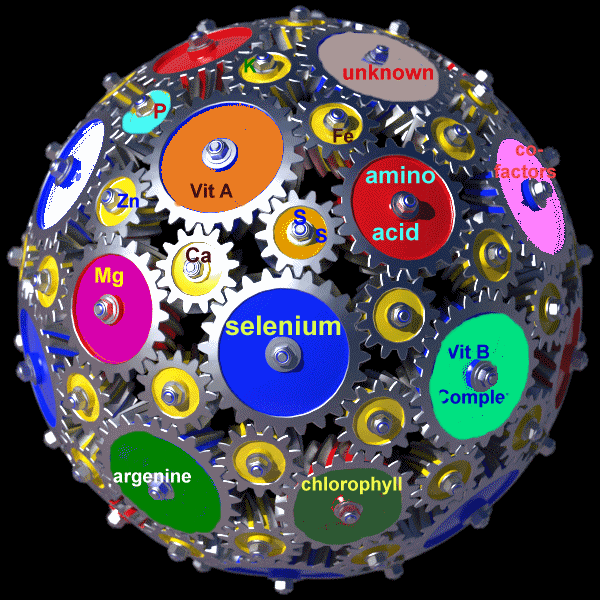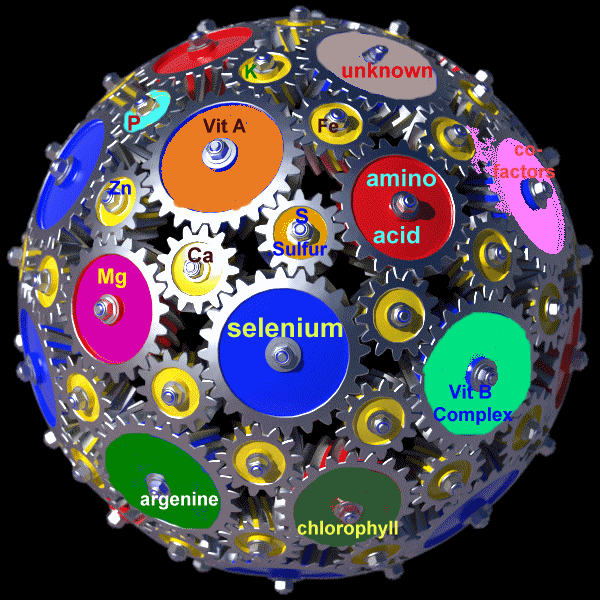 A more extensive picture of the whole food complex is illustrated in the
animation on the right. The big globe represents your body while the
wheels inside represent different substances, enzymes and nutrients. The wheels representing just a few of the possible
thousands of other substances are not only turning but are vibrating with
energy. The turning of the wheels of each substance implies that
they are co-factoring or helping each other do their jobs. If this was
true for you, then you would be in very good health. But if you were
deficient in one of the nutrients, such a deficiency could slow down or even
stop the circles from turning, making you feel sick; or if the deficiency was
prolonged, then perhaps suffer from a serious ailment or disease.
A more extensive picture of the whole food complex is illustrated in the
animation on the right. The big globe represents your body while the
wheels inside represent different substances, enzymes and nutrients. The wheels representing just a few of the possible
thousands of other substances are not only turning but are vibrating with
energy. The turning of the wheels of each substance implies that
they are co-factoring or helping each other do their jobs. If this was
true for you, then you would be in very good health. But if you were
deficient in one of the nutrients, such a deficiency could slow down or even
stop the circles from turning, making you feel sick; or if the deficiency was
prolonged, then perhaps suffer from a serious ailment or disease.
Unrecognized as yet, by nutritionists and many healers, is that active nutrients can chemically vibrate as electronic waves. Resonance makes whole foods living!
The term live foods is used by many advocates of whole foods and needs a short explanation. The claim is made that whole foods are electrically charged and this makes these foods living! This claim is valid. Everything in nature, living and non-living, has natural specific resonant frequencies: Plants and humans resonate [vibrate], that is, communicate by weak electromagnetic frequency waves. Plants can communicate with each other and other living things, including human cells. Creath: sound healing plants Koziolek: phosynthesis signaling Quantum weiriness of plants-animals Jarvis: What is Quantum Entanglement
Such substance resonance information implies that many substances may be helping each other as co-factors but we lack such research to back up such a theory. A good example of missing information is the affect chlorophyll may have on the body. Even though chlorophyll is found in green plants like vegetables, green barley grass, chlorella and spirulina, and that chlorophyll has a high amount of magnesium, information about chlorophyll link to wellbeing is scant!
There is more to understand about the whole food complex. If you are still skeptical about whole food complex and that synthetic vitamins are different from whole food vitamins, then the next section about mirror images should be helpful.
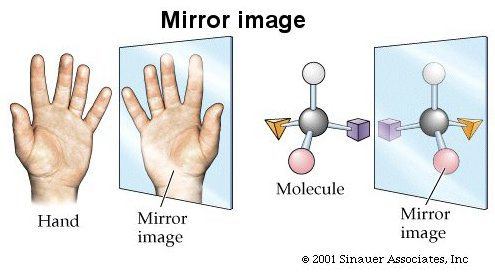 Most biological molecules can take one of two different mirror-image forms.
The mirror image idea is illustrated on the left graphic: When you place
your hand opposite a mirror, the mirror will reflect an image of your hand.
The mirror will reverse the positioning of your hand and we refer to this
display as a mirror image. The left hand is a mirror image of the right hand.
This picture idea is what happens with molecules, amino acids and vitamins. Lets
explore the minor image for amino acids.
Most biological molecules can take one of two different mirror-image forms.
The mirror image idea is illustrated on the left graphic: When you place
your hand opposite a mirror, the mirror will reflect an image of your hand.
The mirror will reverse the positioning of your hand and we refer to this
display as a mirror image. The left hand is a mirror image of the right hand.
This picture idea is what happens with molecules, amino acids and vitamins. Lets
explore the minor image for amino acids.
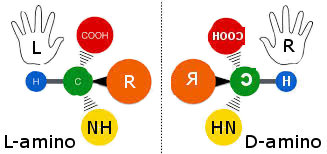
Our bodies can use only amino acids that are of the ‘left-handed’ variety, or L-amino acids [with very rare exceptions]. This effect is known as chirality or mirror image is displayed by Blackman in the image on the right. “L” in this case actually stands for “laevo” not “left”. The other variety is D-amino acids where “D” stands for “dextro”. Both types amino acids have the exact same molecular structure yet they are actually mirror images. The best way to think about the difference is this: your hands may look identical—bones, veins, fingers—yet you can’t put a left-handed glove on your right hand. “L” in this case actually stands for “laevo” not “left”. The other variety is D-amino acids where “D” stands for “dextro”. Both types amino acids have the exact same molecular structure yet they are actually mirror images. The best way to think about the difference is this: your hands may look identical—bones, veins, fingers—yet you can’t put a left-handed glove on your right hand. Blackman: L-amino acids 2015
In order for the human body to use amino acids, these molecules need to fit onto specifically shaped receptors. That’s why a left-handed organism can’t use right-handed amino acids. Because of this L-amino acids only come from natural organic processes, such as enzymatic hydrolyzation [ how nature breaks down proteins ]. Synthetically manufactured proteins produce D-amino acids which may be useful in other functions, but not for life. Article by Hoffman: mirror images molecular chirality is no longer active.
"Chiral connections in living organisms are only found in one mirror form. This is like saying that the body is only made up of left-handed molecules that are mirrored – not right-handed molecules. If a drug is to work optimally it must, metaphorically speaking, be developed as a glove for a left hand; a drug developed for a right hand will not match the molecules." Svane-Knudsen: Mirror images 2011
The information about mirror image is that it can apply to foods, synthetic nutrients and drug medications. If the glove does not fit the mirror imahe of the substance, then the body excretes it! The synthetic form is dangerous because you can get a higher concentrated serving of the artificial vitamin rather than the lesser amount that you would get from a food-based form. The higher dosage is usually without all the supporting co-factors, thereby causing illness and disorders. Group: Differences between at-syn vitamins 2013 Herein lies the crux of the vitamin controversy for the uninformed!
Vitamins can be terrorists:
There is a definite link between vitamin-mineral supplements and whole food complex and it has been a war of misinformation and politics. Woodward: How vitamins are made The problem with vitamin-mineral supplements is that many vitamin and mineral supplements are manufactured in the laboratory synthetically with chemicals that do not come from their natural food sources. Thiel: Truth about vitamins These are made in a lab with the hope that these will mimic the way natural vitamins act in our bodies. Many synthetic vitamins lack the transporter substances and co-factors [ helpers ] associated with naturally-occurring vitamins. Most of these co-factor substances are unknown at this time. Wiki: other nutrients Synthetic vitamins are single substances that have been “isolated” [ removed ] from other supporting substances. There are claims made by those marketing synthetic vitamins that isolated vitamins are used and recognized by the body in the same way as natural versions. This has been researched by scientists to be untrue. "A natural vitamin form comes as a complete package with co-factors, other vitamins, enzymes, substances and minerals in the essential ratio that helps control the way the body recognizes, metabolizes and uses them to make what the body needs." Article by Thiel: Mineral supplements is no longer active. "A whole-food supplement is one comprised of foods (not extracts, but entire foods) that have been concentrated into supplemental form. Isolated supplements are singular [or groups of individual] vitamins, minerals and/or amino acids. Whole foods contain vitamins, but synthetic vitamins never contain the rest of the whole-food "complex". Vitamins never exist in isolation, but rather within an interwoven complex of food nutrients and substances along with myriad cofactors and synergists." Shurtleff: Whole food interpretation of Shayne 2001 Article by Dreher: Whole food supplements is no longer active. Bruce: whole food defined 2000
The body recognizes whole food complexes but not individual, isolate or synthetic chiral mirror images. Synthetic vitamin supplements are recognized by the human body as aliens or toxins and are excreted from the body. No wonder many inept researchers made claims that vitamin C did not work in the body when they used the wrong kind of vitamin C in their research design.
Commercialization of whole food complex
Over 100 nutrition companies are packaging and marketing products in often deceptive labeling ways by saying that their products are whole plant food complex based; bending the real truth! Even the grocery store Whole Foods has latched on to the whole food complex idea, implying that their foods are whole food complexs, in hopes of attracting more food shoppers than their competitors. Core: Whole Foods Store 2014
The use of the wording 'Food-based vitamins' is without a doubt, perhaps the most overused and abused term in the supplements industry. Most companies use this term loosely to describe any vitamin product that is formulated entirely with synthetic isolates, but at the same time include a small amount of fruit or vegetable powders to justify the description "food-based." This kind of labeling is fairly misleading and a disservice to customers who are actually looking for vitamins derived from food sources. If you see a product with a label that says "Food-based," but does NOT list the food source that the vitamins [or other micronutrients] were extracted from, you can be sure that you are NOT getting a true food-based supplement.
"We should be concerned about taking synthetic vitamins and other unnatural nutrients because published research in the last few years concludes two important things: First, synthetic and other unnatural nutrients, masqueraded as real vitamins, are mostly ineffective in keeping us healthy and preventing disease. Second, these synthetic chemicals may be dangerous to your health — some have been shown to increase the risk of death!" Maffetone Dangers synthetic vitamins2008
Recommendations: What should you eat & do?
Whole food supplements are what their name suggests, that is, supplements made from concentrated whole foods. The vitamins found within these supplements are not isolated. They are highly complex structures that combine a variety of enzymes, coenzymes, antioxidants, trace elements, activators and many other unknown or undiscovered factors all working together synergistically, to enable a vitamin complex to do its job in your body.
The best source of vitamins and minerals is from whole food. When we complement our organic whole foods-based diet with supplements, we need to make sure that these vitamins are derived from naturally occurring plant and mineral sources, and that they contain no synthetic chemicals [ nor fertilizers and pesticides ] whatsoever. It may be prudent to add whole-food or spirulina supplements to bolster our diet. You can save money by ingesting spirulina instead of buying vitamins-mineral synthetic supplements. Spirulina is readily absorbed and used in the body whereas synthetic supplements are not bioavailable. Spirulina has a whole-food complex that includes all the supporting vitamins, minerals, amino acids, anti-oxidants and other unknown substances [nutrient-dense] that are in the proper ratios to be used by the body. Spirulina vitamins, minerals, amino acids

 We need to focus on getting Natural vitamins and minerals from whole food vitamins. Eat
foods that have them. Since our soils are mineral depleted and plant vitamins
Brown: status world food 2011
Article by Harrington: soil depletion food is no longer active.
Article by Marler: harvested food quality is no longer active.
may also be of low quality; you may also need to whole food supplement your food diet.
We need to focus on getting Natural vitamins and minerals from whole food vitamins. Eat
foods that have them. Since our soils are mineral depleted and plant vitamins
Brown: status world food 2011
Article by Harrington: soil depletion food is no longer active.
Article by Marler: harvested food quality is no longer active.
may also be of low quality; you may also need to whole food supplement your food diet.
Avoid synthetic vitamin-mineral supplements for obvious reasons! Based upon the findings of this investigation, researcher-author Sorochan advocates the following options:
1. Obtain your nutrients, vitamins, minerals and amino acids as much as you can from whole foods and sunshine. Avoid processed foods, GMO and sugar foods. Avoid fast foods and eating at restaurants where you have little control and knowledge of the food source and quality used. Most restaurants serve meal portions that are too high in calories. Instead, eat home cooked meals where you can have control of the food sources.
2. Be prepared to supplement your diet, as plants grown on depleted mineral soils may not provide adequate nutrient amounts. The following health practices should be better than synthetic supplements:
- 1st choice: Try whole-food supplements if you can find and afford one.
- 1st choice: Sunshine for vitamin D. Depending where you live, your age and the color of your skin, exposure of 15 to 30 minutes per day between 11:00 am and 2:00pm, three times a week, should allow your skin to make all the vitamin D your body needs. You cannot overdose on vitamin D from sunshine; although you can burn your skin if you stay in the sun for a longer time.
- 2nd choice: Ingest barley green grass or spirulina. Both should provide balanced ratios of plant-sunshine derived nutrients and their co-factor helpers. Both are also rich in chlorophyll. Spirulina in tablet form may be tastier to take than barley green grass. Read the labels! All spirulina supplements are not the same and there is controversy about their bioavailability! For example, some spirulina supplements may lack adequate amounts of omega3 and EPA and DHA fatty oils and even a balance of amino acids.
- 3rd choice: Juicing fresh green vegetables and fruits is a great way to get nutrients and chlorophyll. But be aware that it is difficult to get all the nutrients your body needs from a single juicing.
Chlorella, spirulina, vegetables, cereals and barley green grass are created by mother nature as "whole food-complexes." In their natural raw states, these contain all the vitamins, minerals and amino acids in a balanced ratio of co-factors and essential substances [ nutrient-dense ] needed for your body to absorb and use nutrients. Furthermore, both contain chlorophyll that helps body metabolism, fosters the good bacteria in your large intestine, bolsters the immune system and aids in detoxifying toxins. There are no side-effects and both spirulina and barley green grass are safe. Spirulina and/or barley green grass are better as whole-food supplements than commercial vitamin-mineral supplements. But beware of following: The harvesting, processing and packaging of spirulina and barley green grass can destroy many of their natural nutrients and supporting substances. Woodward: How vitamins are made Hopefully this will not be the case in the choice you make.
You need to take charge of your life and manage it! Do not be afraid to try out the recommendations on yourself. Write to your congresspersons and senators for food reforms [ agricultural [DA] subsidies, FDA, NIH, require medical students to take real nutrition courses and provide more independent research grants for nutrient unknowns like chlorophyll.
I fear all of this talk of whole food complex and supplements -- food-based, isolated or synthetic -- may have detracted from the most important part of health and healing. The basics of proper diet, exercise, detoxification, structure, mental/emotional and spiritual health must all be in order for true healing to occur. No supplement will work on its own if these foundations are not in place.
Whole food complex is very much like a jug-saw puzzle. We have many pieces that appear to fit but we only see a small part of the big food and wellbeing picture.
For more information about vitamin-mineral supplements, visit: Whole food complex: Whole food complex
References:
American Association For The Advancement Of Science, "Vitamin C Produces Gene-Damaging Compounds, Test-Tube Study In Science Reports," ScienceDaily. June 15, 2001, Retrieved September 16, 2013. AAAS: Vit C damages 2001
Blackman Caitlin, "L-Amino Acids : What Is Essential & Left Versus Right," Linkedin, April 1, 2015. Blackman: L-amino acids 2015
Brown Lester R., WORLD ON THE EDGE [TEXT] W • W • NORTON & COMPANY New York, 2011. Brown: status world food 2011. Brown: status world food 2011
Bruce Bonnie, Gene A. Spiller, Leslie M. Klevay, Sandra K. Gallagher, "A Diet High in Whole and Unrefined Foods Favorably Alters Lipids, Antioxidant Defenses, and Colon Function," Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 2000, Vol. 19, No. 1, 61–67. Bruce: whole food defined 2000
Chapa Aaron, "Whole Food Vitamins: Ascorbic Acid Is Not Vitamin C," Living Well Nutrition Clinic, August 17, 2011. Chapa: Dr Lee & nutrition 2011
Chong Daniel, "Real or Synthetic: The Truth Behind Whole-Food Supplements," Mercola.com, January 19, 2005. Article by Chong: Whole-food supplements is no longer active.
Clement Bryan, "Nutri-Con: The Truth About Vitamins & Supplements," Organic Consumers Association and Hippocrates Health Institute & OCA, December 31, 2006. Clement: Vitamin truth 2006
Core Liz, "Is the new Whole Foods rating system creating an inferiority complex for zucchini?" Grist, October 15, 2014. Core: Whole Foods Store 2014
Dreher Christine, "Whole Food Supplements The Best Source of Dietary Supplementation." Article by Dreher: Whole food supplements is no longer active.
Duke, James, Handbook of Chemical Constituents of Grasses, Herbs, and other Economical Plants, CRC Press, Boca Raton , 1992.
Harrington Bob and Kelley, "Mineral Erosion From Our Planet's Soil," ZoeLiving, 2007. Article by Harrington: soil depletion food is no longer active.
Hoffman Ronald, "Ronald Hoffmann: Winner of 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry," Darmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science, March 24, 2010. Article by Hoffman: mirror images molecular chirality is no longer active.
Marler John B. and Jeanne R. Wallin, "Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems," Nutrition Security Institute [ Bellvue, Wa.,] 2006. Article by Marler: harvested food quality is no longer active.
O'Shea Tim, "WHOLE FOOD VITAMINS: Ascorbic Acid is Not Vitamin C." O'Shea: Whole food vitamins
Riken research, "A helping hand for proline," August 25, 2006. Riken: Proline mirrors 2006 "amino acids can take one of two different mirror-image forms. Now scientists think they may have found a clue to solve one of the biggest puzzles in science: why only the ‘left-handed’ form of amino acid is found in living systems."
Shayne, Vic, Whole Food Nutrition: The Missing Link in Vitamin Therapy, IUniverse, New York, 2000. Book.
Shurtleff Russell W., "Using Whole-Food Supplements in Clinical Nutrition," Dynamic Chiropractic, March 12, 2001, Vol. 19, Issue 06. Shurtleff: Whole food interpretation of Shayne 2001
Svane-Knudsen Ditte, "Researchers have uncovered an important mechanism that will result in more effective drugs," ScienceNordic, December 8, 2011. Svane-Knudsen: Mirror images 2011
Thiel R.J., "Natural Vitamins May Be Superior to Synthetic Ones," Medical Hypotheses, 2000; 55(6):461-469. Thiel: natural vitamins superior 2000
Thiel Robert, "The Truth About Minerals in Nutritional Supplements," Doctor's Research. Article by Thiel: Mineral supplements is no longer active.
Wikipedia, "Whole food." Wiki: whole food defined
Woodward Angela, "How products are made[vitamins]," Volume 3. Woodward: How vitamins are made